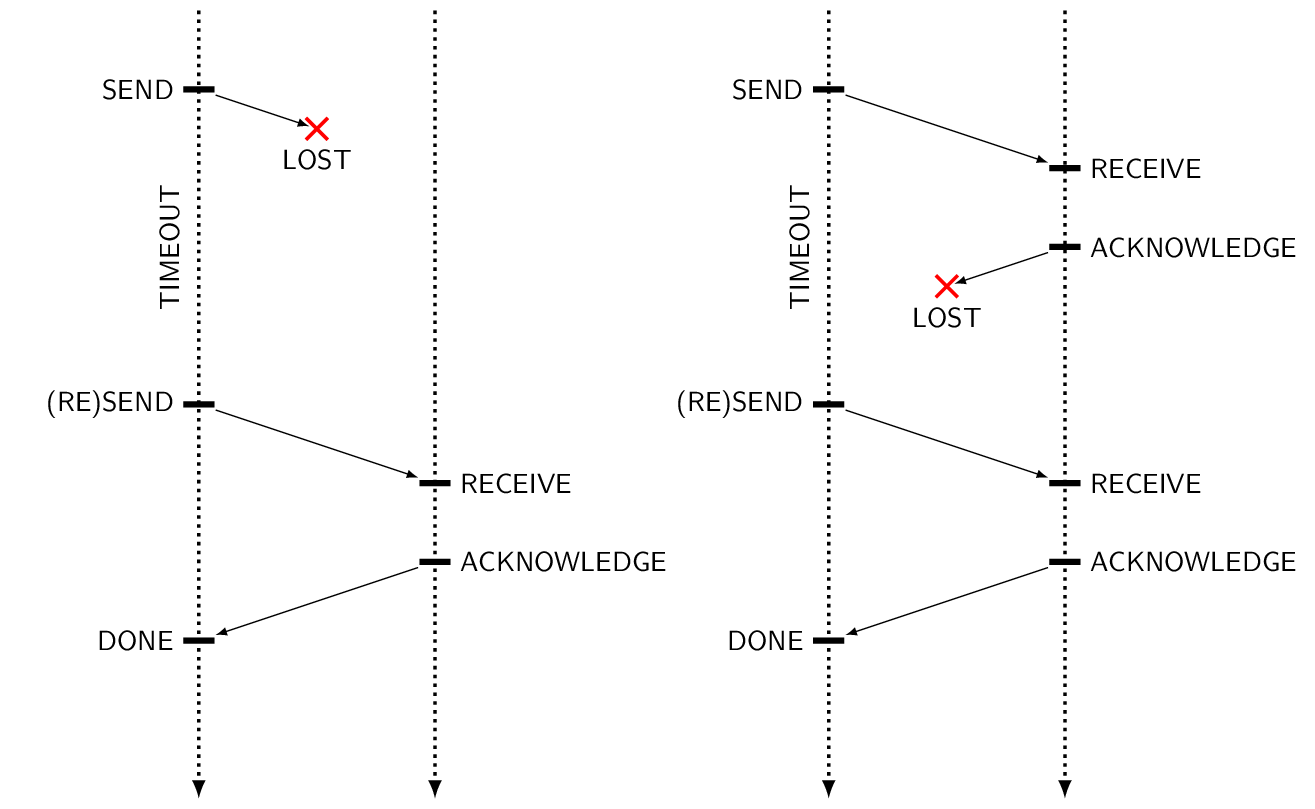
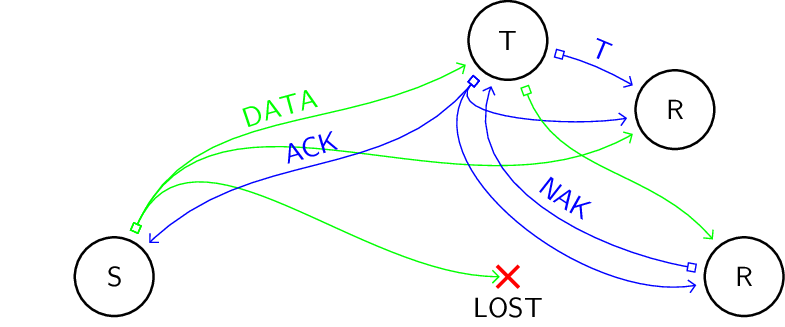
One standard way of ensuring reliable delivery is introducing acknowledgments. Note how the loss of a message and the loss of an acknowledgment cannot be distinguished by the sender. That is why the messages must possess identities, and why amnesia failures, where the record of received message identities is lost, can cause repeated message delivery.
Another way of increasing delivery reliability is forward error correction, where redundant information is transmitted in order to increase the probability of receiving enough information to reconstruct the original message.
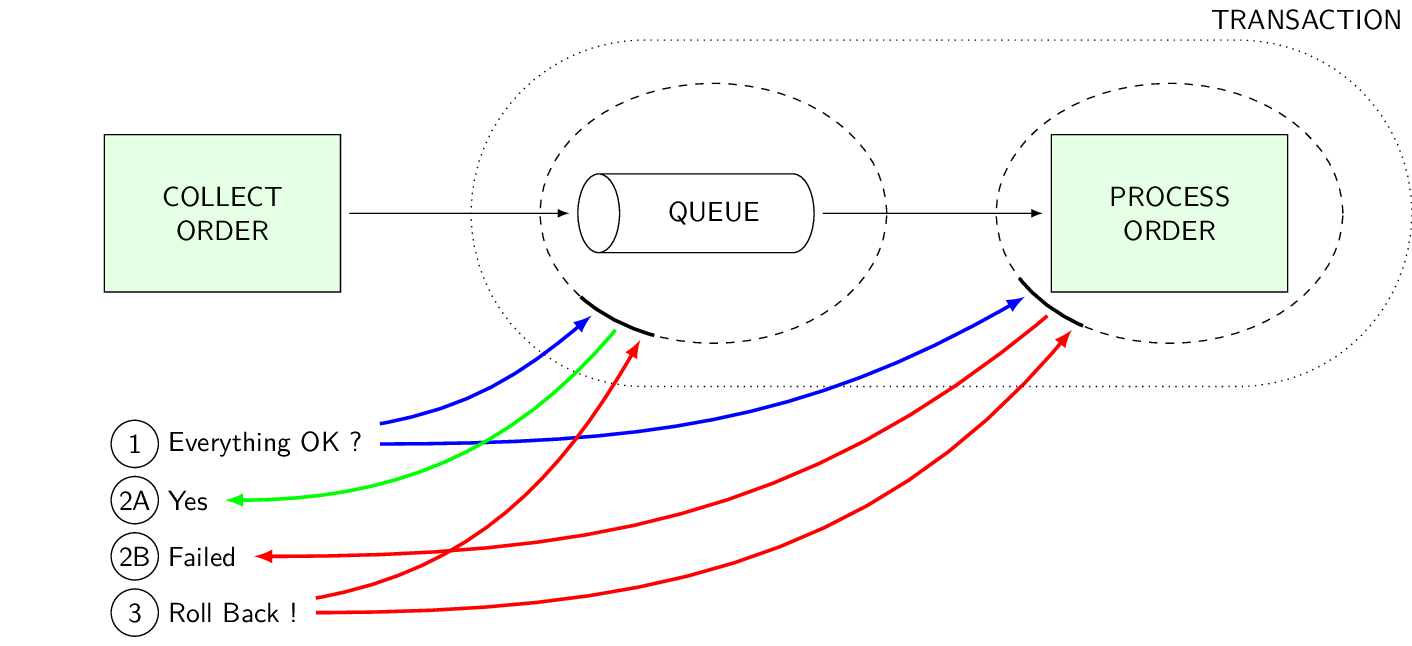
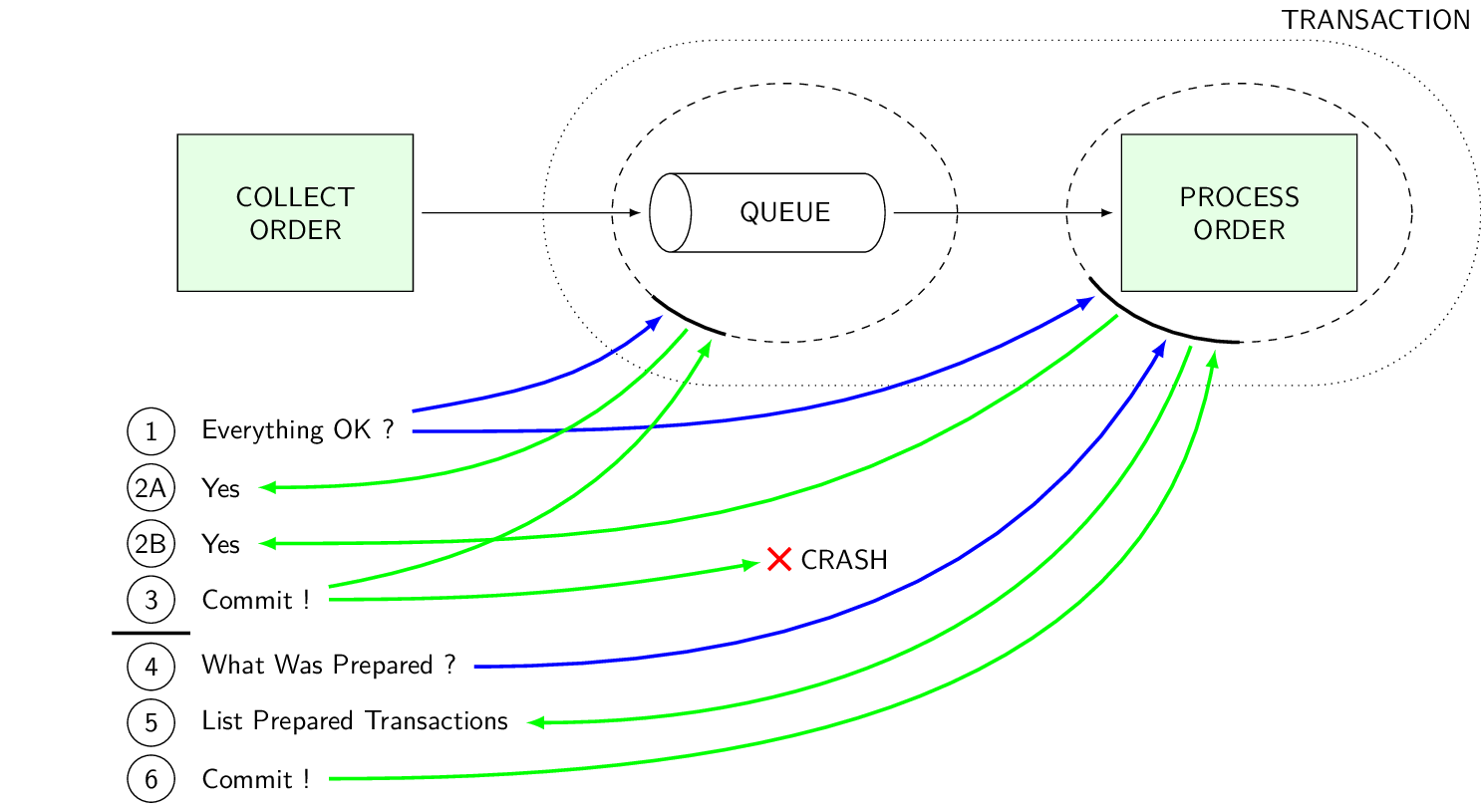
Two phase commit protocol ensures atomic completion of transactions. If any transaction participant fails during transaction, a rollback command is issued to all participants.
If any transaction participant fails after commit has been decided, it must recover and proceed as directed by the coordinator.
In the multicast listener discovery protocol, the router responsible for a link periodically multicasts General Multicast Listener Queries, inviting nodes to report what multicast addresses they listen to. The nodes respond with Multicast Listener Reports, which are multicast after random delay. If a node observes a report with the same multicast address within the random delay, it drops its own report.
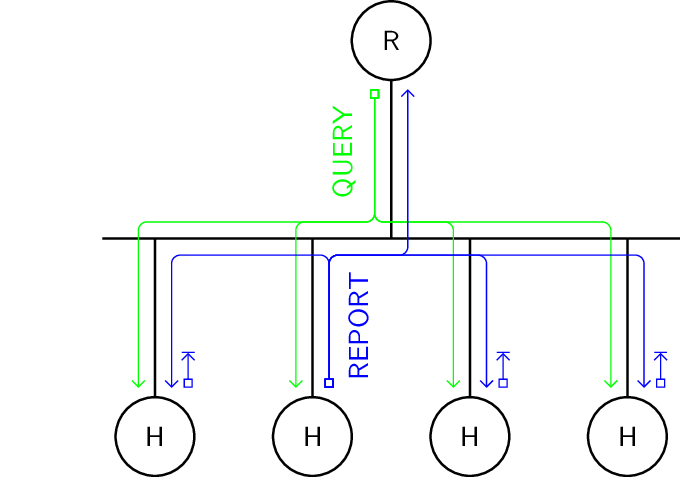
Protocol.
- QUERY
General Multicast Listener Query periodically multicast by router
- REPORT
Multicast Listener Report multicast after random delay
A node that stops listening to a multicast address sends a Multicast Listener Drop message to the router. In response, the router multicasts Specific Multicast Listener Query to inquire about remaining listeners.
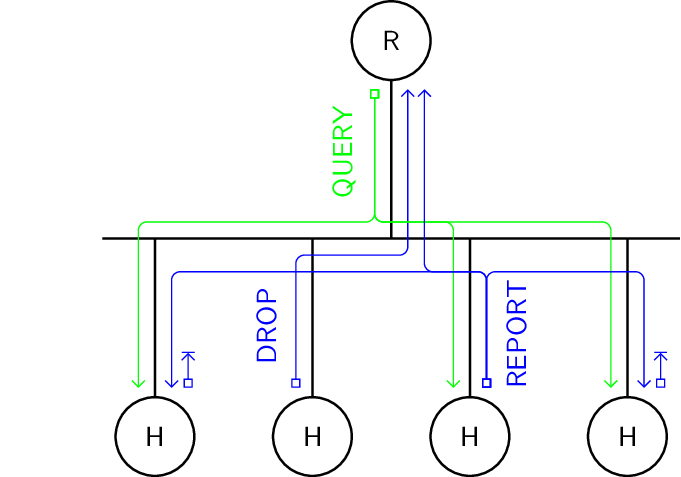
Protocol.
- DROP
Multicast Listener Drop sent from host to routers
- QUERY
Specific Multicast Listener Query multicast by router
- REPORT
Multicast Listener Report multicast after random delay
IETF: Multicast Listener Discovery (RFC 2710). https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2710
In sender initiated error recovery, tracking of lost messages is the responsibility of the sender. To do that, the sender requires a positive acknowledgment from each receiver on message delivery.
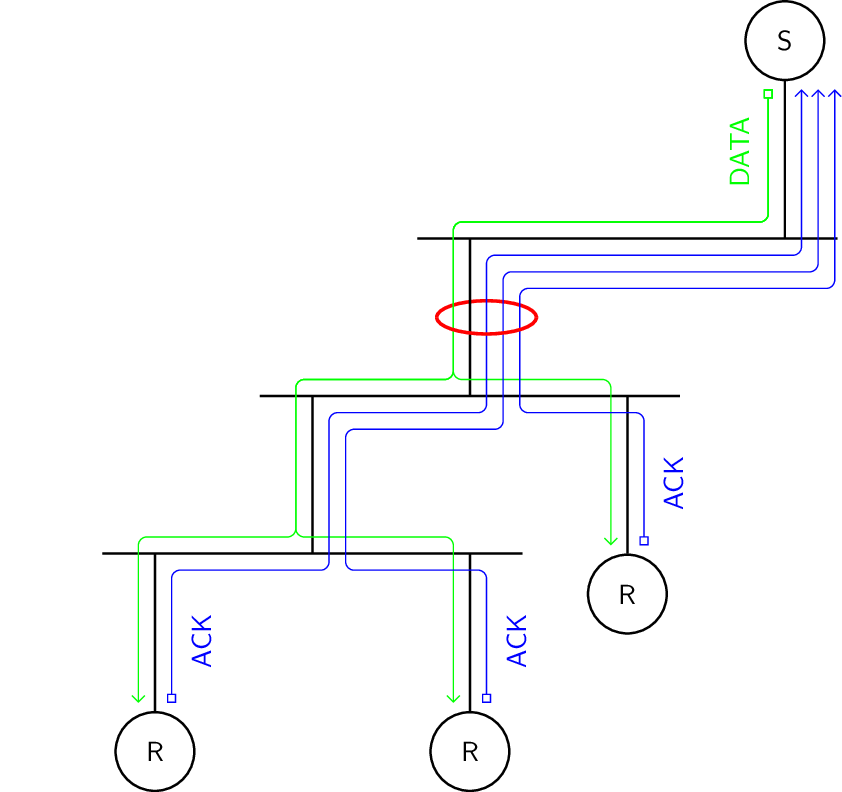
Features.
Can suffer from ACK implosion
Sender must know all receivers
Sender knows when data can be dropped
In receiver initiated error recovery, tracking of lost messages is the responsibility of the receiver. To do that, the receiver transmits a negative acknowledgment on detected message loss.
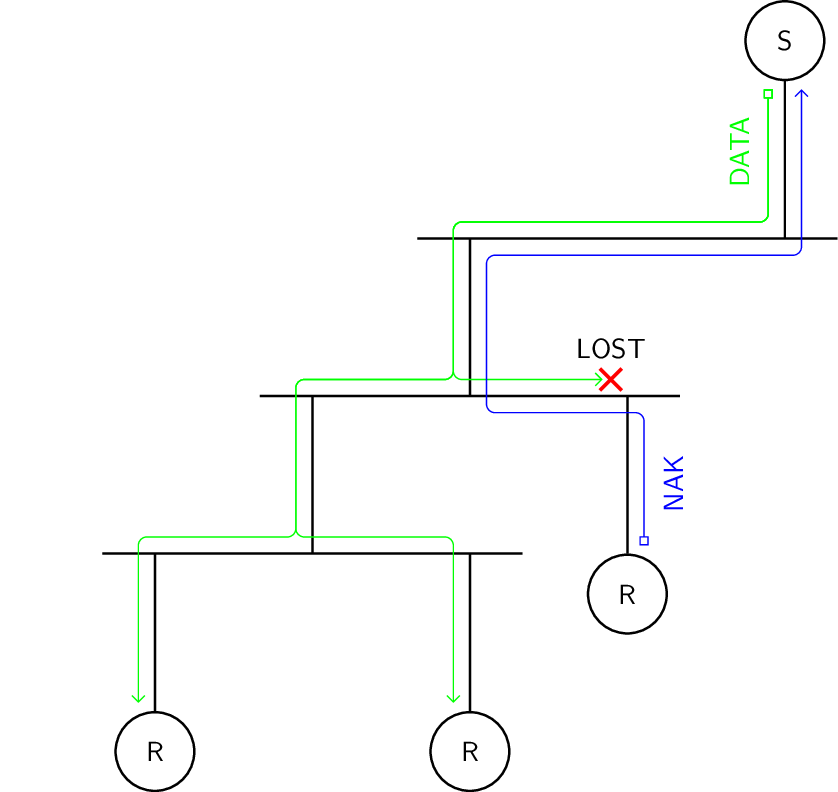
Features.
Can suffer from NAK implosion
Sender must transmit keepalive messages.
Sender does not know when data can be dropped
Acknowledgment messages can be aggregated alongside the network topology.
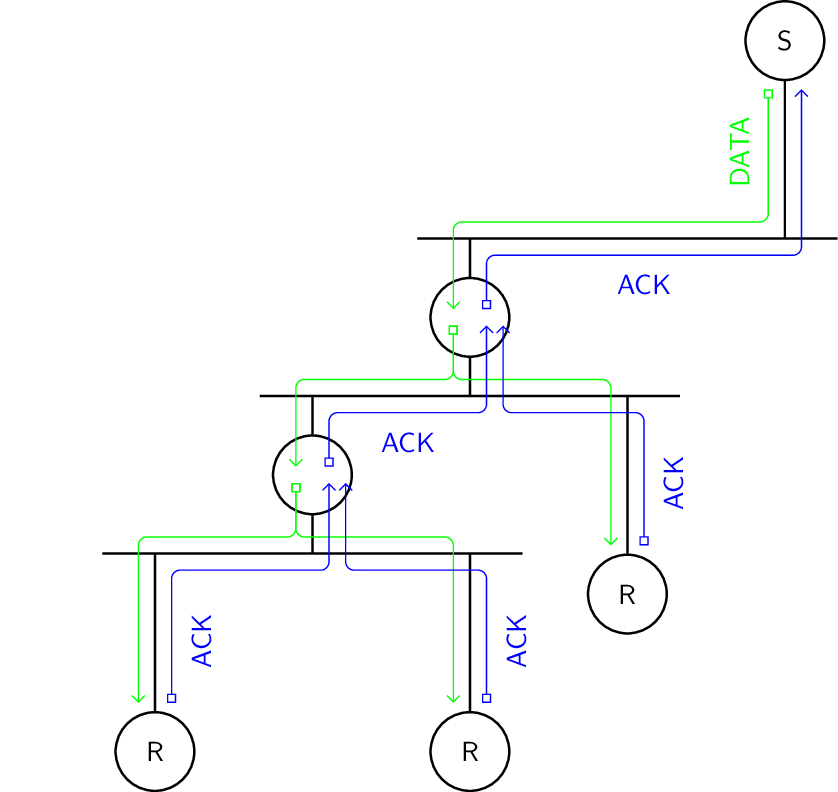
Features.
Multiple variants with different acknowledgments possible
Requires cooperation from network elements
Can be substituted with overlay network
The Pragmatic General Multicast Protocol relies on receiver initiated error recovery with acknowledgment aggregation. Negative acknowledgments are sent to the nearest parent network element along the path, which multicasts confirmation to children along the path, possibly discards redundant negative acknowledgments and forwards to the nearest parent network element along the path again. Repair data packets are routed along reverse path created by negative acknowledgments. A node can also announce itself as a designated local repairer to a local network element. Such network element may forward the negative acknowledgments to the repairer rather than the source.
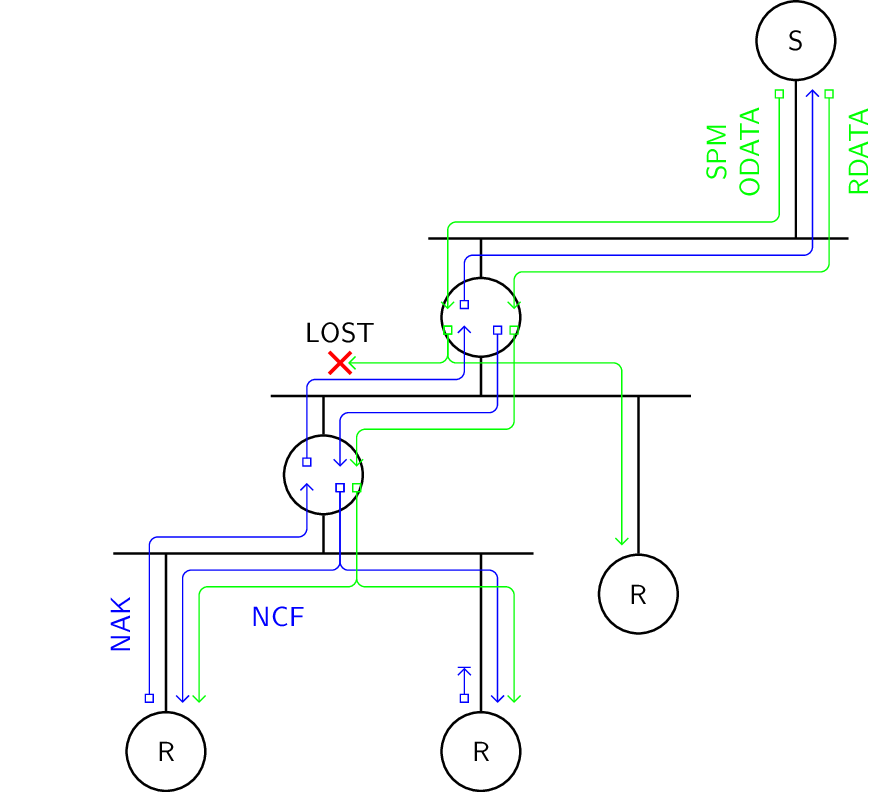
Protocol.
- SPM
Source Path Messages establish path information and perform keepalive function
- ODATA
Original data packets multicast to all receivers
- NAK
Negative Acknowledgment unicast to nearest parent along path
- NCF
Negative Acknowledgment Confirmation multicast to children along path
- RDATA
Repair data packets multicast to selected receivers
For congestion control, the protocol supports adding network load information (observed packet loss rate) to negative acknowledgments. Network elements examine and possibly update the load information when forwarding acknowledgments so that the worst condition in the particular routing subtree is reported upstream. The protocol does not specify the reaction of the source to the network load information.
Additional features of the protocol permit sources to poll network elements or receivers in a randomized manner that prevents response implosion.
IETF: PGM Reliable Transport Protocol Specification (RFC 3208). https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3208
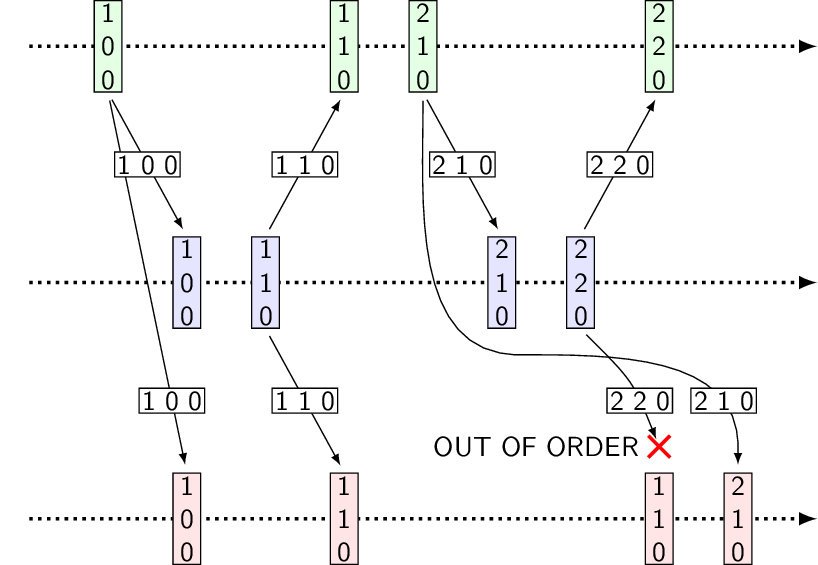
- Source Ordering
Each node defines local order of SEND operations
Message delivery observes union of the local orderings
- Causal Ordering
Each node defines local order of SEND operations
Each node defines local order of RECV-SEND operation pairs
Message delivery semantics defines global order of SEND-RECV operation pairs
Message delivery observes transitive closure of the orderings
- Total Ordering
All nodes observe the same order of SEND and RECV operations
Lamport clock is a type of logical clock that reflects causality in timestamp order.
Vector clock is a type of logical clock that captures causality in timestamp values. When message transmissions are counted as significant events, vector clock can be used to provide causal ordering.
The Token Ring Based Multicast Protocol provides ordering and resiliency guarantees. The current token holder is responsible for totally ordering all messages. The token rotation rules ensure resiliency.